Prismes

Les prismes sont des composants optiques utilisés pour diriger la lumière selon un angle spécifié et peuvent également être utilisés pour séparer la lumière blanche en ses couleurs constitutives par réfraction. Les prismes les plus simples laissent la lumière se propager à travers eux sans réflexion (seulement réfraction), tandis que les prismes plus complexes utilisent plusieurs réflexions internes pour atteindre leur objectif. Les propriétés de la lumière, telles que le retard, peuvent être contrôlées et manipulées grâce à une conception astucieuse du trajet du faisceau interne. OptoSigma propose une large variété de prismes, notamment des prismes équilatéraux, des prismes à angle droit, des prismes à angle droit (revêtus), des prismes penta, des prismes à coin, des réflecteurs rétro-réfléchissants creux, des conduits de lumière, des prismes de Dove, des prismes de Pellin Broca et des prismes à arête tranchante. Si aucun de nos nombreux prismes du catalogue ne répond à vos besoins, veuillez nous envoyer une demande pour un prisme personnalisé.
-
Rétroréflecteur coin de cube
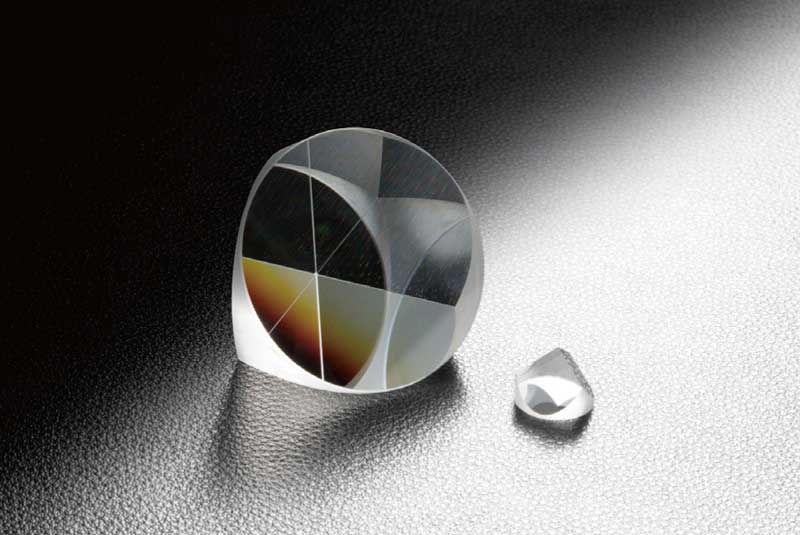

-
Concentrateur parabolique
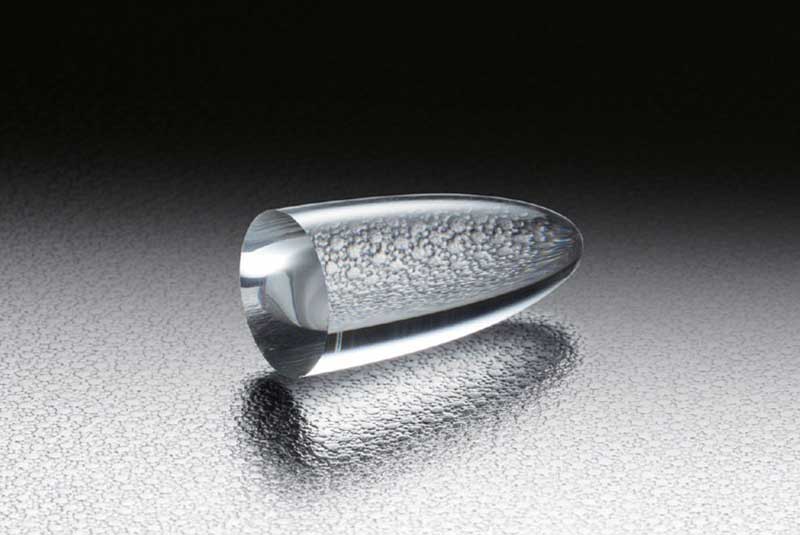

-
Prisme Dove
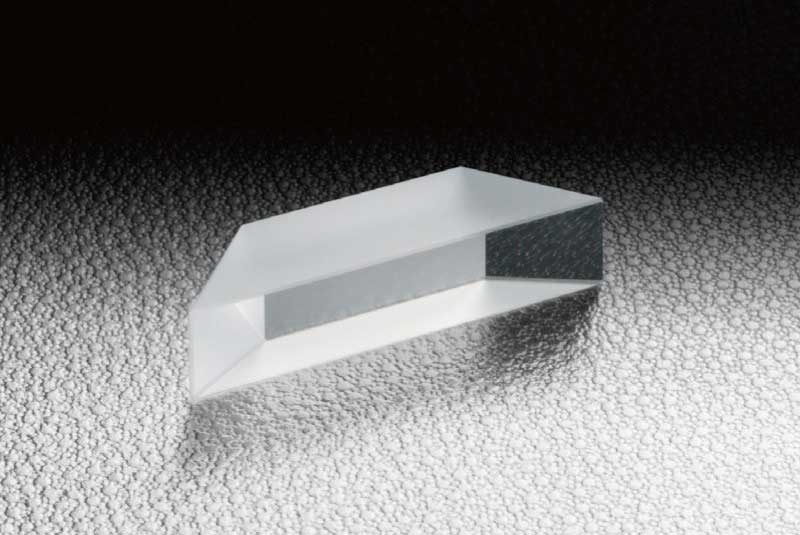

-
Prisme équilatéral disperseur
-
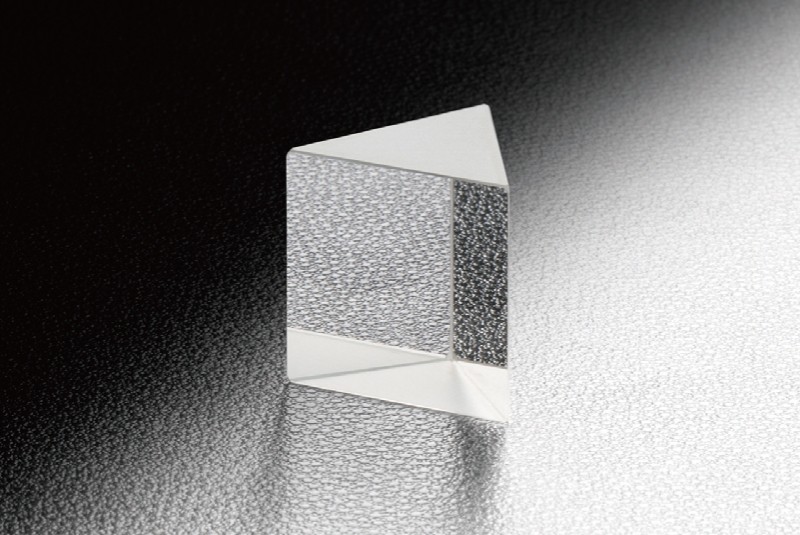
Prisme de Pellin-Broca
-
Pentaprisme

-
Feuille de prisme
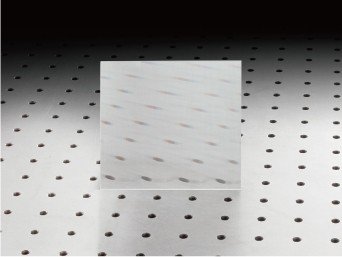
-
Rétroréflecteur creux
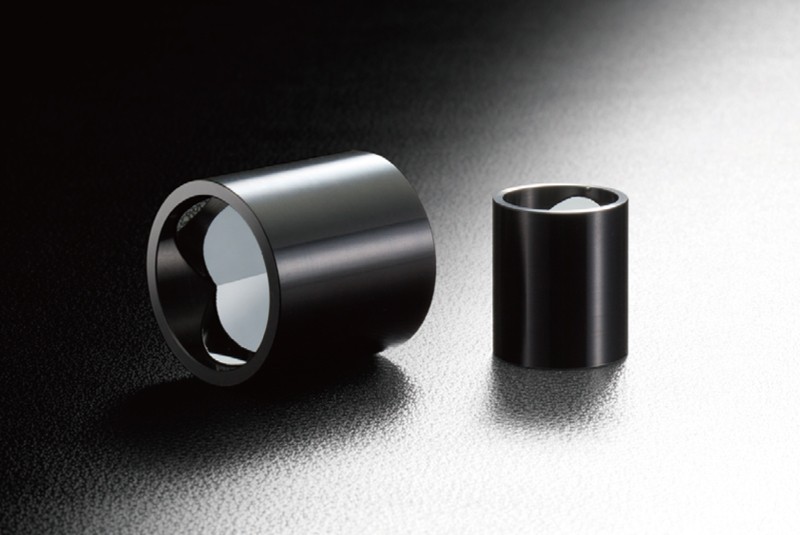

-
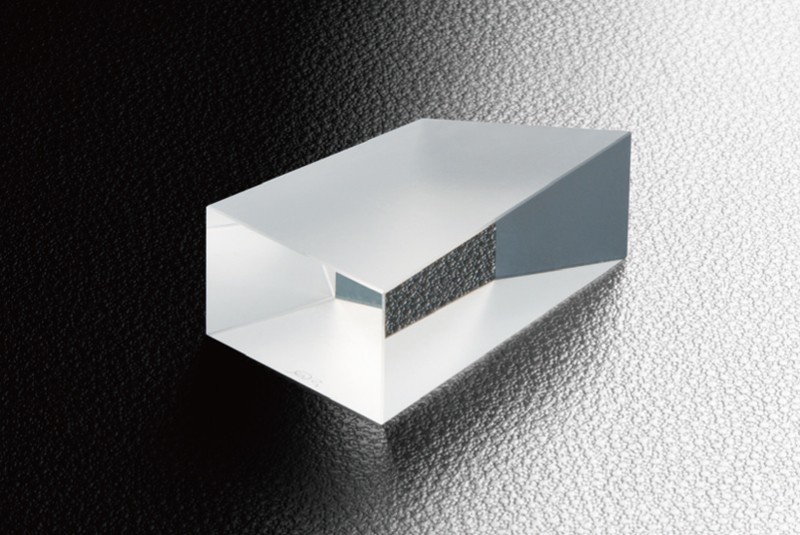
Prisme à angle droit
-
Prismes à arête vive à angle droit
-
Prismes de dispersion de Littrow
-
Contact pour les commandes spéciales de prismes
-
Conduit lumineux
Prisms Application Guide
By processing the various forms of glass, the prism produces a special effect due to refraction. Since there is no angular offset after manufacture, it is also used as an accurate reference angle.
Function |
Product |
Application |
|
Reflecting light |
|
Right Angle Prisms(RPB/RPSQ) |
Substitute of the mirror,or reflector of a compact optical system. |
Replacing the light |
|
Corner Cube Prisms(CCB)Hollow Retro-reflectors(RCCB) |
Interferometer, Reflector, such as distance measurement or delay line. |
Dispersion wavelength |
|
Equilateral Dispersing Prisms(DPB/DPSQ/DPTIH11) |
Spectroscopic measurement, Dispersion compensation |
Special effects |
|
Dove Prisms(DOP), Penta Prisms(PPB), Pellin-Broca prism(PBPQ) |
Rotate or flip the image |
About Refraction and Critical angle
When the light is at an incident oblique angle on the glass, causing the refraction at the interface of the glass and air, the traveling direction of the light will change. At this time, the emission angle toward the side of the glass is smaller than the incident angle of the air. If the refractive index of the glass can be seen, this relationship can be determined by Snell’s law. Then, even if the incident light is emitted at the same angle as the angle θb shown below the boundary surface of the glass, through the same path, it will be emitted to the air at the incident angle θa. However, if it is incident at a large angle with the boundary surface from the side of the glass, then emitted to the air-side angle will exceed 90 degrees. It is called “critical” the emission angle of the air side when 90 degrees. It is called to be this angle “critical angle”. When the incident light from the glass boundary is at an angle larger than the critical angle θr, the light will not come out to the air causing total reflection.






